数据类型包括:基本数据类型和引用类型
# 基本数据类型
基本数据类型又叫值类型,包括StringNumberBooleanNullUndefinedSymbol六种
数值、布尔值、对象和字符串值(没错,每个字符串也都有一个toString()方法,该方法返回字符串的一个副本)都有toString()方法。但null和undefined值没有该方法
# 引用类型
引用类型的值(对象)是引用类型的一个实例。在ECMAScript中,引用类型是一种数据结构,用于将数据和功能组织在一起
对象是某个特定引用类型的实例
常见的引用类型有:
ObjectArrayFunctionDateRegExp
- Object:任意对象
- Array:是一种特别的对象(数值下标,内部数据是有序的)
- Function是一种特别的对象(可执行)
# 判断数据类型
可以通过以下几种方式进行判断数据的类型
- typeof
- instanceof
- toString
- constructor
- ===
# typeof操作符
对于一个值使用typeof操作符可能返回下列某个字符串:
- "undefined"---这个值未定义
- "string"---这个值是字符串
- "number"---这个值是数值
- "boolean"---这个值是布尔值
- "object"---这个值是null或者object
- "function"---这个值是函数
实例
var message;
function w() {
console.log('我是函数')
}
console.log(typeof message); // 'undefined'
console.log(typeof undefined);// 'undefined'
console.log(typeof 123); // 'number'
console.log(typeof 'quman'); // 'string'
console.log(typeof false); // 'boolean'
console.log(typeof null); // 'object'
console.log(typeof {'a': 1}); // 'object'
console.log(typeof(w)); // 'function'
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
typeof是一个操作符而不是函数,因此例子中的圆括号可以尽管使用,但不是必须的,而且返回的是字符串
# instanceof
instanceof运算符用于检测构造函数的prototype属性是否出现在某个实例对象的原型链上,简而言之:用于判断一个引用类型是否属于某构造函数
最简单的就是区分数组、对象、函数
示例
[] instanceof Array // true
[] instanceof Object // true
{} instanceof Array // false
function e() {}
e insatnceof Function // true
e instanceof Object // true
2
3
4
5
6
语法
object instanceof constrcutor
object---某个实例对象
constructor---某个构造函数
描述:instanceof运算符用来检测constructor.prototype是否在于object的原型链上
2
3
4
5
从 instanceof 能够判断出 [ ].proto 指向 Array.prototype,而 Array.prototype.proto 又指向了Object.prototype,最终 Object.prototype.proto 指向了null,标志着原型链的结束。因此,[]、Array、Object 就在内部形成了一条原型链:
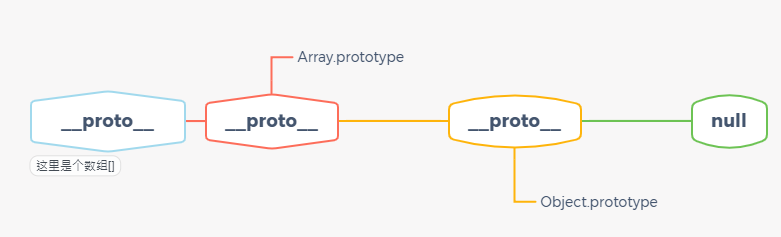
原型链的示例
// 定义构造函数
function C() {}
function D() {}
var o = new C()
o instanceof C // true 因为o._proto_ === C.prototype 或者 Object.getPrototypeOf(0) === C.prototype
o instanceof D // false 因为D.prototype不在o的原型链上
o instanceof Object // true o.__proto__.__proto__ === Object.prototype成立(Object.prototype.isPrototype(o)返回true)
C.prototype instanceof Object // true C.prototype就是o._proto_
C.prototype = {}
var o2 = new C()
o2 instanceof C // true 同上
o instanceof C // false C.prototype 指向了一个空对象,这个空对象不在o的原型链上
D.prototype = new C() // D继承了C
var o3 = new D()
o3 instanceof D // true
o3 instanceof C // true 因为c.prototype现在在o3的原型链上
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
一些容易出错的点
String对象和Date对象都属于Object类型的一些特殊情况
示例如下
var simpleStr = "This is a simple string";
var myString = new String();
var newStr = new String("String created with constructor");
var myDate = new Date();
var myObj = {};
var myNonObj = Object.create(null);
simpleStr instanceof String; // 返回 false, 非对象实例,因此返回 false
myString instanceof String; // 返回 true
newStr instanceof String; // 返回 true
myString instanceof Object; // 返回 true
myObj instanceof Object; // 返回 true, 尽管原型没有定义
({}) instanceof Object; // 返回 true, 同上
myNonObj instanceof Object; // 返回 false, 一种创建非 Object 实例的对象的方法
myString instanceof Date; //返回 false
myDate instanceof Date; // 返回 true
myDate instanceof Object; // 返回 true
myDate instanceof String; // 返回 false
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
Object.create()方法创建对象时添加的属性是在原型下面的
new Object() 通过构造函数来创建对象,添加的属性是在自身实例上
示例如下
// Object.create() 方式创建
var a = { rep: 'apple' }
var b = Object.create(a)
console.log(b) // {}
console.log(b.__proto__) // {rep: "apple"}
console.log(b.rep) // {rep: "apple"}
// new Object() 方式创建
var a = { rep : 'apple' }
var b = new Object(a)
console.log(b) // {rep: "apple"}
console.log(b.__proto__) // {}
console.log(b.rep) // {rep: "apple"}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
手动实现一下instanceof的功能
function myInstanceof(left, right) {
let L = left.__proto__;
const R = right.prototype
// 基本数据类型直接返回false
if (left=== null || typeof left !== 'object') return false
while(true) {
// 查到尽头还没找到
if (L === null) return false
// 找到相同的原型对象
if (L === R) return true
L = L.__proto__
}
}
验证代码
function C() {}
var o = new C()
console.log(myInstanceof('111', String)) // false
console.log(myInstanceof(new String('11111'), String)) // true
console.log(myInstanceof(o, C)) // true
console.log(myInstanceof([], Array)) // true
console.log(myInstanceof([], Object)) // true
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# toString
Object.prototype.toString.call()是最准确最常用的方式,首先获取Object原型上的toString方法,让方法执行,让toString方法中的this指向第一个参数的值
关于toString的重要补充
- 本意是转换为字符串,但是某些toString方法不仅仅是转换为字符串
- 对于
Number、String、Boolean、Array、RegExp、Date、Function原型上的toString方法就是把当前的数据类型转换为字符串类型(作用仅仅是转换为字符串类型) - Object上的toString并不是用来转换字符串的,它的作用返回当前方法执行的主体(方法中的this)所属类的详细信息即“
[object Object]”,其中第一个object代表当前实例是数据对象类型的(这个是固定死的),第二个Object代表的是this所属的类是Object
示例
Object.prototype.toString.call('') // "[object String]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(1) // "[object Number]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(true) // "[object Boolean]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(undefined) // "[object Undefined]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(null) // "[object Null]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(new Function()) // "[object Function]"
Object.prototype.toString.call([]) // "[object Array]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(new Date()) // "[object Date]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(new RegExp()) // "[object RegExp]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(new Error()) // "[object Error]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(document) // "[object HTMLDocument]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(window) // "[object Window]"
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# constructor
constructor是原型prototype的一个属性,当函数被定义的时候,js引擎会为函数添加prototype,并且这个prototype中constructor属性指向函数引用,因此重写prototype会丢失原来的contructor
null和undefined无constructor
('123').constructor // ƒ String() { [native code] }
([]).constructor // ƒ Array() { [native code] }
(1).constructor // ƒ Number() { [native code] }
({}).constructor // ƒ Object() { [native code] }
(null).constructor // Uncaught TypeError: Cannot read property 'constructor' of null
// 用法
'123'.constructor === String // true
new Number(333).constructor === Number // true
true.constructor === Boolean // true
[].constructor === Array // true
new Object().constructor === Object // true
new Date().constructor === Date // true
new Error().constructor === Error // true
window.constructor === Window // true
document.constructor === HTMLDocument // true
new Function().constructor === Function // true
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 严格运算符 ===
用于判断全等
null === null // true
undfined === undfined // true
2
# 特殊场景
特殊场景1: null和undefined
null值表示一个空对象指针,undefined表示一个值未定义
// 关系判断
console.log(null == undefined) // true undefined派生自null
console.log(null == undefined) // false
console.log(null == false) // false
//转为number类型
console.log(Number(null)) // 0
console.log(Number(undefined)) // NaN
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
特殊场景2:NaN
NaN即非数值(Not a Number)是一个特殊的数值,用于表示一个本来要返回数值的操作数未返回数值的情况,比如任何数值除以0会返回NaN。
NaN两个特性:
- 任何涉及NaN的操作都会返回NaN
- NaN与任何值都不相等,包括NaN本身
实例:
console.log(Number('hello world')) // NaN
console.log(parseInt('')) // NaN
console.log(Number(.12)) // 0.12
console.log(parseInt('.12')) // NaN
2
3
4